The Real Internet Capital Markets: Rise of Compliant Crypto-Native Fundraising Platforms
The emergence of compliant crypto-native fundraising platforms marks a pivotal shift in capital formation. Recent developments, such as Coinbase's $375 million acquisition of Echo (a platform founded by Cobie) and Kraken's partnership with Legion to launch "Kraken Launch," signal the maturation of onchain fundraising. These moves highlight a growing trend toward regulated, accessible platforms that bridge traditional markets with blockchain, reducing friction while enhancing global participation.
Traditional methods like stock offerings and venture capital enable investors to gain equity stakes, potentially earning dividends or profits from resale. However, they are plagued by inherent limitations: (1) rigidity – inflexible bureaucratic and regulatory processes; (2) high costs – financial burdens; and (3) exclusivity – limited access in selected regions. These barriers limit opportunities for retail investors and smaller startups, creating an uneven playing field.
Blockchain fundraising has existed since the 2017 ICO boom, with platforms like Pump.fun and Believe.app enabling crypto token launches in recent market cycles. However, these platforms face significant regulatory hurdles, as many of the tokens launched on them may constitute securities, leading to lawsuits and compliance challenges.
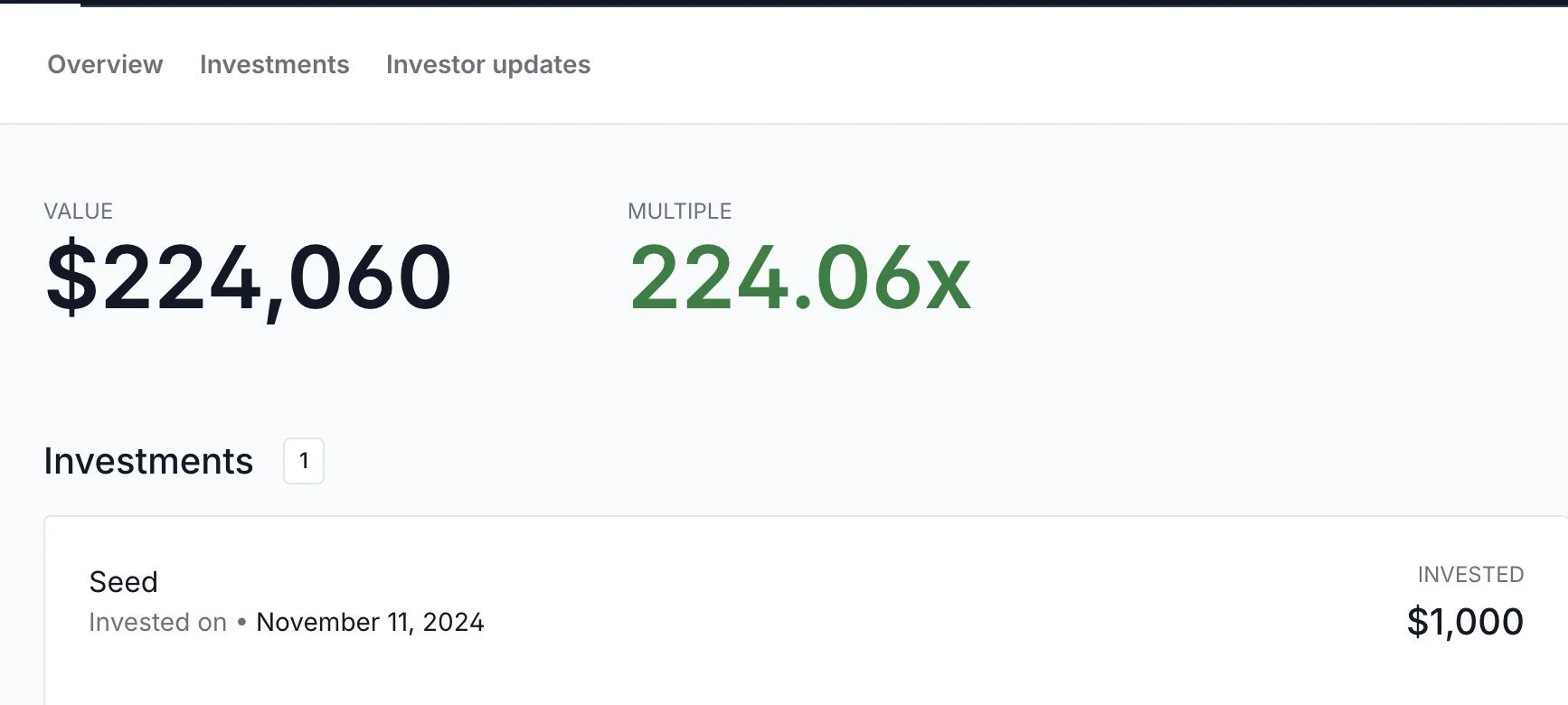
By 2023-2025, platforms like Echo and Legion have pioneered compliant alternatives, leveraging smart contracts for transparent, efficient capital raises. Echo began as a private investment group but evolved with the launch of Sonar in May 2025, a self-hosted public sale tool enabling compliant token offerings. Sonar's debut facilitated Plasma's $XPL token, raising funds instantly for a stablecoin-focused blockchain, with small participants (those that contributed $1) earning an airdrop of worth $10,000. Following this, MegaETH – a much-anticipated blockchain hyped on crypto twitter, scheduled its public ICO on Sonar on October 27.
Link to original post: https://x.com/postedgo/status/1971251179591254384
These platforms (Echo and Legion) are catalyzing the rise of regulated Internet Capital Markets (ICM), blockchain-native systems for seamless, jurisdiction-compliant fundraising. ICMs democratize access, allowing accredited investors worldwide to participate in top-tier crypto startups, majority of which are limited to U.S. based and other well-known VCs. Majority of the capital raised are via SAFTs, granting investors the right to receive tokens at a later date. Unlike stocks, tokens don't represent company ownership but form a distinct asset class with advantages like 24/7 trading, instant settlement, and programmability.
These types of crypto fundraisings that happen in Echo and Legion align with crypto's decentralization ethos, enabling startups to raise funds globally from crypto natives, reaching audiences from every part of the world and improving on token holder count, while adhering to regulations like KYC and AML.
ICMs lower entry barriers compared to traditional markets: (1) Accessibility – Global reach for retail (Echo’s Sonar and Kaito’s Yap Launchpad) and accredited investors (Echo’s and Legion’s Private Sales); (2) Efficiency – blockchain automate processes, reducing costs and timelines; (3) Innovation – tokenized assets and RWAs (real-world assets) open new opportunities. However, risks persist. Early-stage investments often fail. Personally, I've seen only 3 out of 10 succeed without going to zero, two of those traded below its latest private sale valuation. Crypto's volatility, regulatory shifts, and potential for scams demand due diligence. Platforms like Echo and Legion mitigate some issues through compliance, but investors must remain vigilant.
As Coinbase integrates Echo's tools (starting with Sonar) and Kraken expands via Legion, ICMs could redefine capital markets, blending TradFi stability with DeFi innovation. For startups and investors alike, compliant platforms like these are not just tools: they're the future of equitable capital access.